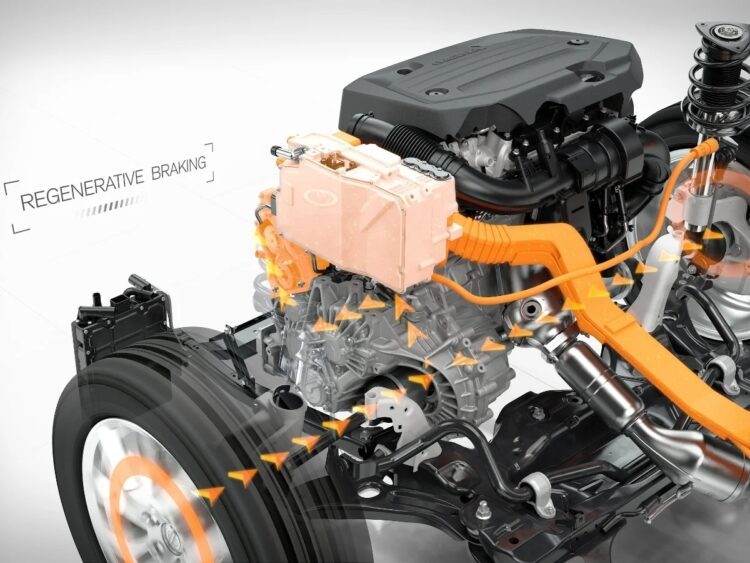
The Regenerative Braking System (RBS) is an advanced method to charge EVs while in use. It is mostly found in electric vehicles and hybrid vehicles. This method is a brilliance of the energy storage system in EVs as regenerating energy in fuel cars is not quite possible.
‘Electricity’ is a high-grade energy while ‘Heat’ is a low-grade energy, which assists the EVs in building the regenerative braking system.
Let’s unearth the physics behind the RBS!
How does a car Engine work?
Usually, when you are driving a car, you immediately hit the brakes with a view of a red light. When your car stops all of a sudden, the energy it has been building ever since it started gets wasted. To start again, the car engine needs to begin building up the kinetic energy again from scratch.
To make it simpler, just imagine riding a bicycle. You start developing a greater pace, only when you take no pause. Once you stop, you need to start peddling again, gradually. It’s not possible the maintain the pace like earlier, suddenly after you start over again. It’s because, when the brake stops the wheel, there is friction caused. This friction converts kinetic energy into heat energy. And further, this heat vanishes into the air, thus, wasting all the energy.
A similar notion happens with a car. The kinetic energy that the car motion has been building disappears in the air after the motion stops. That’s because it causes a loss of kinetic energy in the form of heat. Here, comes the role of electric energy in EVs.
How does Regenerative Braking System work?
So far, we know that electricity makes high-grade energy, unlike heat. So, in electric vehicles, motors become consumers as well as producers of electricity.
While driving an EV, the battery discharges energy to the motor. This creates motion in the wheels by turning on the kinetic force. However, when one hits the brake, an exact inverse situation takes place. The electronic circuits detach the motor power and the wheels dry the motors. Now, the motors start working like generators, making them producers of electricity. The power from the motors flows down to recharge the main battery pack of the EV.
Additionally, this also extends the driving range of the EV by reversing and storing the energy. All in all, the regenerative braking system saves the energy used while stopping the motor get rather than getting wasting it.
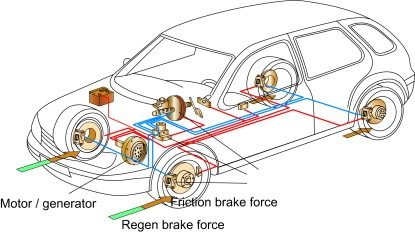
Application of Regenerative Braking System
The occurrence of regeneration happens in the RBS whenever the driver hits the brake. It also takes place when the driver frees the accelerator pedal and the EV is gliding in the air. So, this system acts perfectly in sloppy areas too.
On the whole, the sole motive of electric and hybrid vehicles is saving energy, and with this regenerative braking system, this kind of vehicle can entirely stand up to its purpose.
Efficiency of RBS
Although the term regeneration tends to captivate minds, the actual measurement of this regeneration acts vital. How much regeneration of the energy happens, is a real question.
To date, the RBS has become successful in recovering up to 70% of the kinetic energy. An EV or a hybrid vehicle would otherwise lose this energy, had this system not existed.

Limitations of RBS
Every good thing has some bad elements that cannot be neglected as it might cost you your life, plus, others’ life. The Regenerative Braking System definitely has some flaws stocked. To point out a few:-
- There is a severe drop in effectiveness during the slower speed.
- The sensations of the brake might not be well-responsive at times.
- As a result of the friction brake, the system might hold to lose the braking ability itself if the RBS fails.
- RBS addition to a vehicle increases its curb weight.





