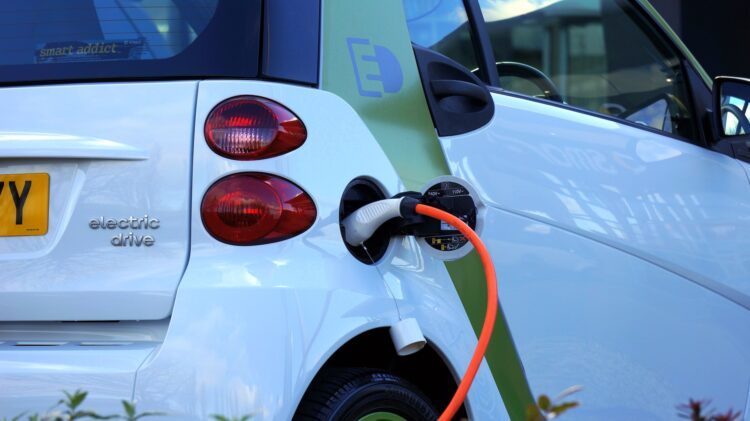
One must discuss modern motor vehicles, including electric automobiles. They represent the latest generation of electric vehicles (EVs) in the automotive sector, powered by rechargeable batteries and solely run on electricity. EVs are becoming increasingly common in Nepal, with a sizable amount of hydroelectricity potential.
Introducing EVs in Nepal was to lessen the environmental harm caused by combustion-powered vehicles. Vehicles that use burning fuels to drive the engine which creates hazardous waste gases, such as carbon dioxide, are a substantial source of environmental pollution. For this reason, major nations worldwide are pushing for electric vehicles to replace gasoline-powered vehicles as the norm in terms of mainstream modes of transportation.
Continuing the same trend, Nepal has seen a rise in EVs. Undoubtedly, Nepal’s EV adoption has brought a wealth of prospects, but to capitalize on those possibilities, the nation must also overcome many obstacles. For example, electric vehicles’ motors are powered by lead-acid, lithium-ion nickel-hydrated batteries; these batteries are made to store a lot of power while they are being charged, which can start the car. Therefore, in Nepal, switching to electric vehicles is a great idea because they also have a lot of advantages.
Electric Vehicle Policy in Nepal
Since electric cars don’t emit exhaust waste, the Nepali government promotes them as it does in most other places to lessen the environmental impact of fossil fuels. The government has directly impacted EV imports in Nepal through its revenue strategy to discourage the use of fossil fuel vehicles. In addition, the Government of Nepal announced a policy that will permit combustion vehicles to be converted to electric vehicles. Nepal has much potential to import and employ electric vehicles, beginning with expanding operations for the thriving economy. The majority of automotive enthusiasts now favor electric vehicles.
EV Data in Nepal
Over the past six months, it has seen a surge in the importation of electric vehicles due to the Nepali government lowering taxes. According to reports, it imported over 1,350 electric vehicles in December 2021, nearly five times as many as it did during the previous fiscal year when it imported only about 250 electric vehicles.
Expanding its global market is an opportunity because it may allow importing electric automobiles. Despite having among the quickest economies, Nepal has a small wage of roughly $36.168 billion and an annual revenue per capita of $1,155.10 in 2019–2020. Even though the hospitality industry makes up a larger share of Nepal’s GDP, agriculture still substantially impacts the country’s economy. Since they run on electricity, they require little upkeep.
However, they are exceedingly difficult to utilize as everyday automobiles due to their extensive maintenance requirements, which can cost as much as a gasoline-powered automobile.
Additionally, Nepal has a modern, well-developed network that can help with the seamless integration of these vehicles. They do not perform well on tough, uneven terrain, but the wonderful, straight road does. The administration must now focus on finding solutions to these problems.





